In today’s fast-paced and increasingly complex business environment, companies of all sizes need efficient systems to manage their operations. One of the most valuable tools in this regard is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software. ERP systems integrate various core business functions into one unified platform, allowing companies to streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and improve overall performance. This article will provide an overview of ERP software, its components, benefits, and how businesses can leverage it to gain a competitive edge.
What is ERP Software?
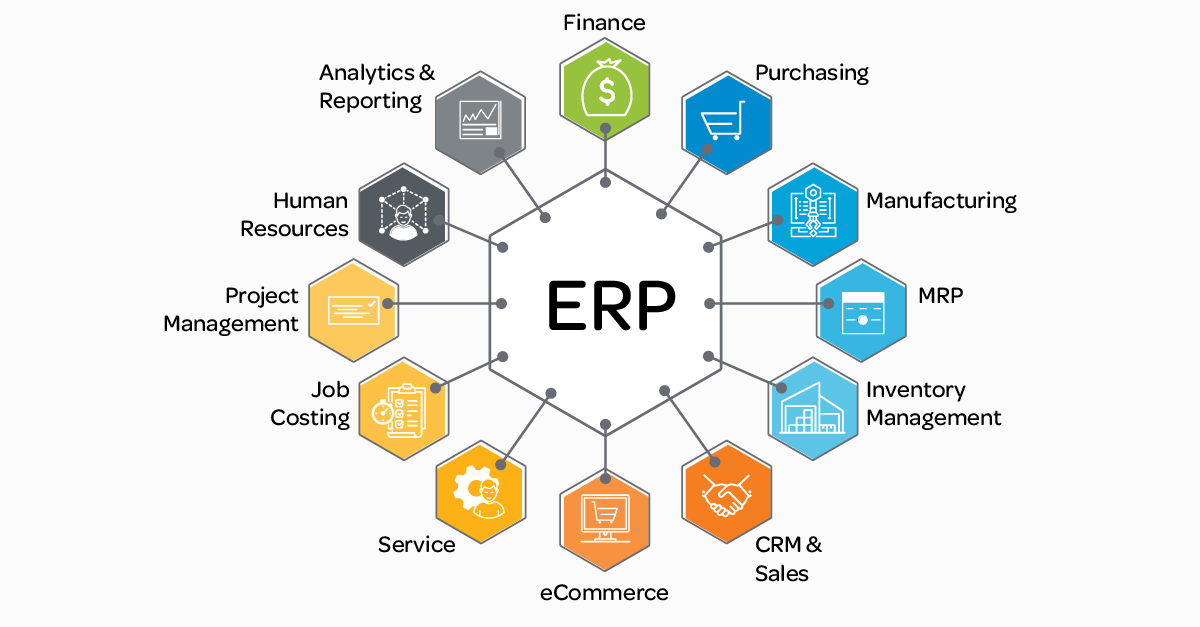
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a type of business management software that integrates and automates essential business processes such as accounting, procurement, inventory management, human resources (HR), sales, and customer relationship management (CRM). By centralizing data into a single system, ERP software enables businesses to achieve greater efficiency, reduce errors, and ensure that information is readily available across all departments.
Typically, ERP systems consist of a suite of applications designed to manage specific business functions, all working together on a unified platform. These systems allow businesses to track and manage data in real time, offering enhanced visibility into business performance and enabling better decision-making.
Key Components of ERP Software
An ERP system is made up of several core modules, each focusing on different business processes. Some of the key components include:
- Accounting and Financial Management: The financial module of an ERP system helps businesses manage their accounting processes, including accounts payable and receivable, general ledger, payroll, and financial reporting. It ensures that all financial transactions are accurately recorded, and financial reports are generated in real time.
- Inventory and Supply Chain Management: ERP software helps businesses manage their inventory levels, orders, and procurement processes. It can track stock levels, orders, and shipments, allowing businesses to optimize supply chain operations. This module helps prevent stockouts, reduce excess inventory, and streamline purchasing processes.
- Human Resources (HR): The HR module handles various aspects of human resource management, including payroll, recruitment, benefits administration, performance management, and compliance with labor regulations. It streamlines HR operations, improves employee satisfaction, and ensures the smooth functioning of the workforce.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): The CRM module helps businesses track and manage customer interactions. It includes tools for managing sales, marketing, customer support, and communication. A CRM system integrated into an ERP solution enables businesses to provide personalized services, track leads, and maintain stronger relationships with customers.
- Sales and Marketing: The sales and marketing module allows businesses to manage their sales pipeline, track customer orders, and improve customer engagement. It helps businesses monitor their sales performance, generate quotes, process orders, and manage marketing campaigns.
- Manufacturing and Production Management: For manufacturing businesses, the ERP system can help manage the production process. It can track production schedules, monitor work orders, manage equipment maintenance, and ensure that the production process is efficient and cost-effective.
- Project Management: This module allows businesses to manage complex projects, including budgeting, scheduling, resource allocation, and tracking project progress. It helps businesses keep projects on track, meet deadlines, and optimize resource usage.
Benefits of ERP Software
ERP software offers a wide range of benefits to businesses, which include:
- Improved Efficiency: One of the primary benefits of ERP systems is the increased efficiency it brings to business operations. By automating key processes, businesses reduce manual tasks, minimize errors, and streamline workflows. This leads to faster decision-making and more efficient resource management.
- Centralized Data: With ERP software, businesses have access to a centralized database, meaning all departments work with the same up-to-date information. This eliminates data silos and ensures that employees can access the most accurate and timely information when making decisions.
- Better Decision-Making: ERP software provides businesses with real-time data and analytics, allowing decision-makers to gain insights into key performance indicators (KPIs), trends, and business performance. This helps management make informed, data-driven decisions and adjust business strategies as needed.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Because ERP systems provide a unified platform, different departments within a business can collaborate more effectively. For example, sales teams can access real-time inventory data, while finance teams can track expenses and revenue. This collaborative approach fosters better communication between teams and ensures that everyone is working toward the same goals.
- Cost Savings: By automating processes and improving operational efficiency, ERP systems help businesses save costs in various areas, such as inventory management, procurement, and human resources. For example, the system can help prevent overstocking or stockouts, reducing the need for excessive storage costs or last-minute purchasing.
- Regulatory Compliance: ERP software helps businesses comply with industry regulations by ensuring that all business processes are recorded and tracked in a standardized way. Many ERP systems are designed with built-in compliance features, such as audit trails and secure data storage, that help businesses meet regulatory requirements.
- Scalability: Modern ERP systems are highly scalable, meaning businesses can easily adapt and expand their ERP software as they grow. Whether adding new modules or increasing the number of users, ERP solutions can scale to meet the needs of businesses of any size, ensuring that the system remains useful as the company evolves.
Types of ERP Software
There are several different types of ERP systems available, each designed to meet the specific needs of businesses in different industries and sizes. These include:
- On-Premises ERP: On-premises ERP software is installed and maintained on a company’s own servers. Businesses that opt for this solution are responsible for managing the system, including updates, security, and IT infrastructure. On-premises ERP can offer more control and customization but requires a significant upfront investment in hardware and IT resources.
- Cloud-Based ERP: Cloud ERP software is hosted on the cloud and accessed via the internet. This type of ERP system is often subscription-based, reducing the need for upfront investment in hardware. Cloud ERP systems are easier to implement, provide automatic software updates, and offer access from any device with an internet connection.
- Hybrid ERP: Hybrid ERP systems combine both on-premises and cloud-based elements. This allows businesses to maintain some processes locally, while benefiting from the flexibility and scalability of the cloud. Hybrid ERP is often chosen by organizations that need to comply with industry regulations but still want the advantages of cloud computing.
Choosing the Right ERP Software for Your Business
When choosing an ERP system, businesses need to consider several factors, including:
- Business Size and Needs: ERP solutions vary in terms of complexity and scalability. Smaller businesses may opt for a simple, cloud-based ERP solution that can grow with them, while larger enterprises may need a more complex, on-premises system with highly customized modules.
- Customization and Flexibility: Some businesses require highly customized ERP solutions to meet specific needs. It’s important to choose a system that can be tailored to your company’s unique processes, whether it’s industry-specific or based on your business model.
- Integration: ERP systems must integrate seamlessly with other software used by the company, such as CRM software, e-commerce platforms, or legacy systems. Compatibility and ease of integration are crucial for minimizing disruptions during implementation.
- Vendor Reputation and Support: When selecting an ERP vendor, businesses should consider the vendor’s reputation, the level of customer support they offer, and their experience in the industry. A reliable vendor will provide adequate training, troubleshooting, and software updates, ensuring the long-term success of the system.
Conclusion
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software is a vital tool for businesses looking to streamline operations, improve collaboration, and make data-driven decisions. Whether it’s for managing financials, inventory, human resources, or customer relationships, ERP software provides businesses with a unified system that simplifies complex processes and improves efficiency. By choosing the right ERP system tailored to their specific needs, businesses can enhance their operations, reduce costs, and stay competitive in an ever-changing market.